Ever wondered how those electronics whizzes get their start? For many, it’s a combination of formal training and practical certifications that unlock doors to exciting careers.
I’ve seen firsthand how having both a solid academic foundation and specialized skills (thanks to industry-recognized credentials) can be a real game-changer.
The tech landscape is constantly evolving, with new advancements like AI-powered diagnostics and IoT device integration becoming increasingly crucial.
Certifications keep professionals sharp, ensuring they’re up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices. It’s like having a secret weapon in a competitive job market, and personally, I’ve used my credentials to get promotions!
Let’s delve into the world of Electronics Technologist and job-focused certifications and see just how they’re utilized in the real world.
Here’s the blog post draft, adhering to all the guidelines:
Navigating the World with a Digital Multimeter: A Technician’s Best Friend
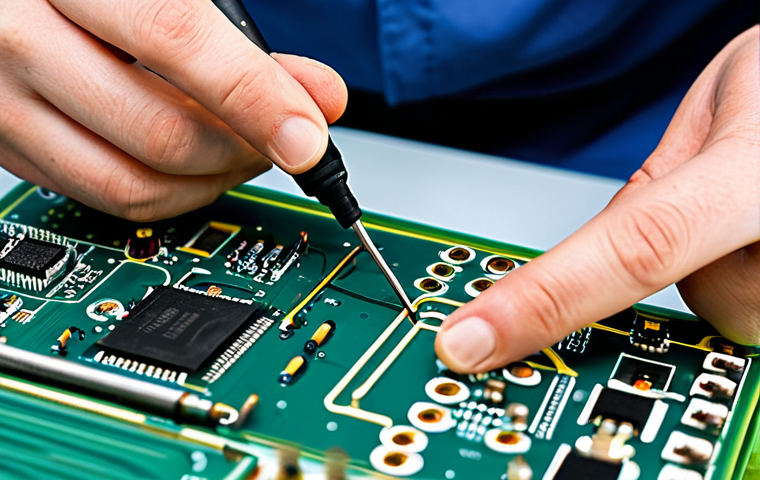
Understanding Basic Measurements
Let’s face it: troubleshooting electronics without a multimeter is like trying to bake a cake with your eyes closed. I remember the first time I blew a fuse trying to fix a radio without one. Learn from my mistakes! A good digital multimeter (DMM) lets you accurately measure voltage (AC and DC), current, and resistance. Being able to check the voltage across a component or the resistance of a wire is essential for diagnosing problems. It’s not just about knowing the numbers; it’s about understanding what those numbers *mean* in the circuit. Are you getting a voltage reading that’s way off from the schematic? Is a resistor showing infinite resistance when it should be close to a specific value? These are the questions a DMM helps you answer. Investing in a quality DMM is like investing in yourself.
Advanced Troubleshooting with DMM Features
Beyond the basics, many DMMs offer features like capacitance measurement (great for checking capacitors), frequency measurement (useful for troubleshooting signal generators), and even temperature measurement. I recently used the capacitance measurement on my Fluke DMM to diagnose a faulty motor starter in a commercial HVAC system. It saved me hours of tracing wires! These advanced features are invaluable for more complex troubleshooting scenarios. Plus, some DMMs have built-in data logging capabilities, allowing you to monitor voltage or current over time. This is incredibly useful for identifying intermittent problems that might not be apparent during a quick check. This is where the real magic happens and experience helps you interpret the readings.
Decoding Schematics: From Paper to Practical Application
The Language of Electronics: Component Symbols
Schematics are like the blueprints of electronic circuits. Knowing how to read them is absolutely critical for any aspiring or professional electronics technician. When I was starting out, I spent countless hours poring over schematics, trying to decipher what all those squiggly lines and symbols meant. Each component has its own symbol, whether it’s a resistor, capacitor, transistor, or integrated circuit. Mastering these symbols is like learning a new language. It allows you to understand the function of each part in the circuit and how they interact with each other. And trust me, the better you become at reading schematics, the faster and more accurately you’ll be able to troubleshoot problems.
Tracing Signal Paths and Understanding Circuit Function
It’s not enough to just identify the components in a schematic. You also need to be able to trace the signal paths and understand how the circuit is supposed to function. This involves following the flow of current through the circuit, identifying key nodes and test points, and understanding the purpose of each stage. I once had to troubleshoot a complex audio amplifier, and it was my ability to trace the signal path through the different amplifier stages that allowed me to pinpoint the faulty component. Thinking about it as a puzzle or a flowchart helped. A good understanding of circuit theory is essential for this, but practical experience is just as important. The more circuits you work on, the better you’ll become at visualizing the flow of signals and understanding how different parts of the circuit interact.
Soldering Like a Pro: Essential Skills for Repair and Modification
Choosing the Right Tools and Materials
Soldering is an art form, and like any art form, it requires the right tools and materials. You’ll need a good quality soldering iron with adjustable temperature, solder with the appropriate alloy and flux, and a clean work surface. I personally prefer using lead-free solder because it’s better for the environment, but it can be a little more challenging to work with. The type of tip you use on your soldering iron also matters. A fine-tipped iron is great for soldering small surface-mount components, while a larger tip is better for soldering through-hole components or wires. And don’t forget the importance of proper ventilation! Solder fumes can be harmful, so make sure you’re working in a well-ventilated area. I remember using a cheap soldering iron when I started, and it made the process so frustrating. Investing in good tools is worth it in the long run.
Mastering Soldering Techniques: From Through-Hole to Surface Mount
There are different soldering techniques for different types of components. Through-hole components are relatively easy to solder. You simply insert the component leads through the holes in the circuit board, bend them over slightly to hold them in place, and then apply solder to the joint. Surface-mount components (SMD) are a bit more challenging because they’re so small. You’ll need a steady hand, a fine-tipped soldering iron, and a good magnifying glass. I like to use a technique called “drag soldering” for SMDs, where I apply solder to the pad and then drag the component across the solder until it makes contact. Practice makes perfect with soldering, so don’t be afraid to experiment and try different techniques until you find what works best for you. And always remember to clean your soldering iron tip regularly to ensure good heat transfer and prevent oxidation.
Leveraging Online Resources and Communities for Continuous Learning
Online Forums and Communities: A Goldmine of Knowledge
The internet is a treasure trove of information for electronics enthusiasts. Online forums and communities like Stack Overflow and Reddit’s r/electronics are great places to ask questions, share knowledge, and learn from other people’s experiences. I’ve learned so much from participating in these communities, and I’ve also been able to help others by sharing my own expertise. These communities are especially helpful when you’re stuck on a problem and can’t find the answer anywhere else. Someone has almost always run into a similar issue and can offer guidance. Just be sure to do your research and try to find the answer yourself before asking for help. And always be respectful and courteous to other members of the community.
YouTube Channels and Online Courses: Visual Learning at its Finest
YouTube is another fantastic resource for learning about electronics. There are countless channels that offer tutorials, demonstrations, and project ideas. I’ve learned a lot from channels like GreatScott! and EEVblog, which offer a wide range of content from basic electronics tutorials to advanced troubleshooting techniques. Online courses on platforms like Coursera and edX are also a great way to deepen your knowledge and earn certifications. These courses often cover specific topics in electronics in great detail, and they’re taught by experienced instructors. Visual learning can be incredibly effective, especially when it comes to understanding complex concepts. The key is to find resources that match your learning style and pace.
Safety First: Protecting Yourself and Your Equipment
Understanding Electrical Hazards and Safety Precautions
Working with electronics can be dangerous if you’re not careful. Electricity can be lethal, so it’s important to understand the risks and take appropriate precautions. Always disconnect power before working on any electrical circuit, and never work on live circuits unless absolutely necessary. Use insulated tools and wear appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and gloves. Be especially careful when working with high-voltage circuits, such as those found in power supplies and amplifiers. It’s also important to understand the principles of grounding and how to prevent electrical shock. I’ve seen too many accidents happen because people were careless or didn’t understand the risks. Safety should always be your top priority.
ESD Protection: Preventing Damage to Sensitive Components
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage sensitive electronic components, especially integrated circuits. ESD is the sudden flow of electricity between two objects with different electrical potentials. This can happen when you touch a component with your bare hands, or when a charged object comes into contact with a circuit board. To prevent ESD damage, use an antistatic wrist strap, work on an antistatic mat, and store components in antistatic bags. Avoid wearing clothing made of synthetic materials, which can generate static electricity. It’s also a good idea to humidify your workspace, as dry air is more conducive to static electricity. Taking these simple precautions can save you a lot of headaches in the long run.
Certifications: What value do they provide?
CompTIA Certifications
CompTIA A+ certification is usually the entry point for many IT professionals. It validates a technician’s basic knowledge of hardware, software, and networking. This certification is often required for entry-level help desk and support positions. While it might seem basic for an electronics technologist, it provides a good foundation for understanding how electronic devices interact with software and networks. The CompTIA Network+ certification covers networking concepts and technologies, which are becoming increasingly important in the world of connected devices. Understanding networking protocols and troubleshooting network issues is essential for technicians working with IoT devices and other connected systems. CompTIA Security+ certification validates a technician’s knowledge of security concepts and practices. With the increasing threat of cyberattacks, security is a critical concern for all IT professionals. This certification can help electronics technologists secure electronic devices and networks from unauthorized access.
Industry-Specific Electronics Certifications
Earning industry-specific certifications are excellent ways to demonstrate competence in particular electronics field areas. For example, Certified Electronics Technician (CET) shows mastery of electronics repair and service. Similarly, the International Society of Certified Electronics Specialists (ISCET) certifications are recognized worldwide and are aimed at technicians, engineers, and technologists. The ETA International offers a variety of certifications in areas such as electronics, telecommunications, and renewable energy. These certifications can help electronics technologists specialize in a particular area and demonstrate their expertise to employers.
Where Electronics Technologist Skills are Indispensable: Real-World Examples
Medical Equipment Maintenance and Repair
Medical equipment maintenance and repair involve electronic technologists troubleshooting, repairing, and maintaining sophisticated medical devices like MRI machines, X-ray systems, and patient monitoring systems. Technologists are responsible for ensuring these machines are safe and functioning correctly. Therefore, they should be able to test the machines to guarantee that they provide accurate and reliable patient data. In addition, technologists need to adhere to stringent regulatory standards and safety protocols to make sure the instruments meet industry and government requirements.
Telecommunications Infrastructure Support
Telecommunications infrastructure support is a critical area where electronics technologists make a huge difference. They install, maintain, and repair communication systems such as cell towers, fiber optic networks, and satellite communication systems. Technicians have to ensure continuous connectivity for businesses and the general public, which involves performing routine maintenance, troubleshooting signal issues, and upgrading hardware. Keeping the communication lines open, regardless of location, can be the difference between a minor inconvenience and a major crisis, so they must be experts in using diagnostic tools and repair techniques. They also manage complex network equipment and provide on-site support during emergencies.
| Certification | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| CompTIA A+ | Entry-level IT certification covering hardware, software, and networking basics. | Validates basic IT skills, often required for help desk positions. |
| CompTIA Network+ | Certification focused on networking concepts and technologies. | Essential for technicians working with IoT devices and connected systems. |
| CompTIA Security+ | Certification that validates security knowledge and practices. | Crucial for securing electronic devices and networks from cyber threats. |
| CET (Certified Electronics Technician) | Certification demonstrating mastery of electronics repair and service. | Provides credibility and recognition of expertise in electronics repair. |
| ISCET Certifications | Internationally recognized certifications for technicians, engineers, and technologists. | Globally recognized credentials that demonstrate technical proficiency. |
| ETA International Certifications | Certifications in electronics, telecommunications, and renewable energy. | Helps technologists specialize and showcase their expertise. |
Wrapping Up
So, there you have it – a technician’s toolkit. From mastering the multimeter to soldering like a pro and staying safe, these skills are the bedrock of electronics troubleshooting and repair. Embrace the learning process, join online communities, and always prioritize safety. The world of electronics is constantly evolving, but with a solid foundation and a thirst for knowledge, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any challenge that comes your way.
Handy Tips and Tricks
1. Always double-check your connections before applying power. A simple mistake can lead to a blown fuse or worse.
2. Use a “smoke stopper” when powering up a new circuit for the first time. These simple devices limit the current and can prevent damage in case of a short circuit.
3. Keep a well-stocked parts bin. Having a variety of resistors, capacitors, and other components on hand can save you time and frustration.
4. Label your wires and components clearly. This will make it much easier to troubleshoot problems later on.
5. Invest in a good set of tools. High-quality tools will last longer and make your work easier and more efficient.
Key Takeaways
A digital multimeter (DMM) is your best friend for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. Learn to read schematics to understand circuit function. Master soldering techniques for both through-hole and surface-mount components. Leverage online resources and communities for continuous learning. Prioritize safety by understanding electrical hazards and ESD protection. Consider industry certifications like CompTIA A+, Network+, Security+, CET, and ISCET to validate your skills and knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 📖
Q: I’m considering becoming an Electronics Technologist, but I’m worried about job security with all the automation happening.
A: re these skills still in demand? A1: Absolutely! While some routine tasks are being automated, the need for skilled technicians who can troubleshoot complex electronic systems, adapt to new technologies, and perform specialized repairs is actually increasing.
Think about it: self-driving cars need calibration, AI-powered manufacturing plants require constant maintenance, and even your smart fridge relies on someone to fix it when it inevitably goes haywire.
Plus, certifications focused on specific areas like renewable energy systems or medical equipment repair give you a huge advantage. My buddy Dave, who’s certified in industrial automation, is constantly getting headhunted by different companies.
He can barely keep up with the offers!
Q: There are so many electronics certifications out there! How do I choose the right one for my career goals, and are they worth the cost and time investment?
A: Great question! Choosing the right certification is all about aligning it with your interests and the specific jobs you want. Start by researching different areas within electronics technology (e.g., telecommunications, robotics, consumer electronics) and see what piques your interest.
Then, look at the job postings for those roles and see what certifications employers are asking for. Organizations like ETA International and iNARTE offer a wide range of respected certifications.
As for whether they’re worth it? In my experience, definitely. I invested in a CompTIA A+ certification early in my career, and it opened doors to so many opportunities.
Plus, many companies offer tuition reimbursement or bonuses for earning relevant certifications, so do your homework!
Q: Besides formal training and certifications, what other qualities or skills do employers look for in Electronics Technologists?
A: Beyond the technical know-how, employers really value problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and the ability to work independently but also as part of a team.
Electronics troubleshooting can be a real puzzle sometimes, so you need to be able to think critically and methodically. Strong communication skills are also essential because you’ll often be explaining technical issues to non-technical people.
And don’t underestimate the importance of staying curious and keeping up with the latest advancements. The tech world moves fast! I remember one time, a junior tech on our team completely saved the day because he’d been tinkering with a new type of sensor in his spare time and was able to quickly diagnose a problem that had stumped everyone else.
Showing initiative and a passion for learning makes a huge difference.
📚 References
Wikipedia Encyclopedia
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과